vscode-fortran-support


Key Features
- Syntax highlighting (Free and Fixed forms)
- Hover support, Signature help and Auto-completion
- GoTo/Peek implementation and Find/Peek references
- Project-wide and Document symbol detection and Renaming
- Native Language Server integration with
fortls - Linting support: GNU’s
gfortran, Intel’sifort,ifx, NAG’snagfor - Interactive Debugger with UI
- Formatting with findent or fprettify
- Code snippets (more can be defined by the user see)
Get Started & Seek Support
Useful Tools
Language Server integration
The Fortran Language Server fortls is responsible
for providing a lot of the higher level, IDE functionality. By default,
Modern Fortran will attempt to use it for hover, autocompletion, symbols and Go to & Peeking into definitions.
Allow for fortls to be automatically installed with pip or Anaconda and
if the location where fortls is installed is not in your PATH point VS Code
to the fortls location by setting
{
"fortran.fortls.path": "/custom/path/to/fortls"
}
For more about the Language Server’s capabilities please refer to the
documentation of fortls.
Linting
Linting allows for compiler error and warning detection while coding without the user having to compile.
| Vendor | Compiler |
|---|---|
| GNU | gfortran |
| Intel | ifort, ifx |
| NAG | nagfor |
Using an invalid if expression
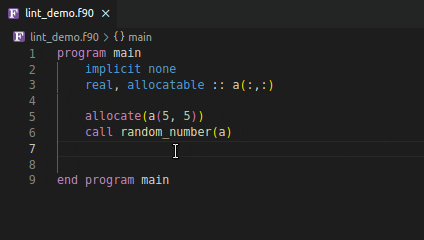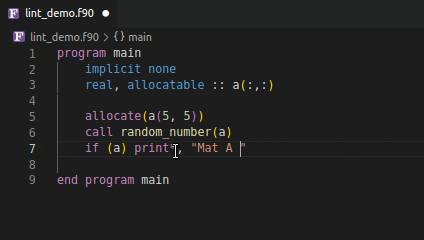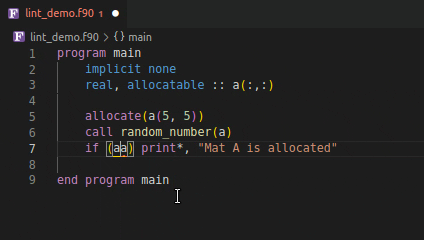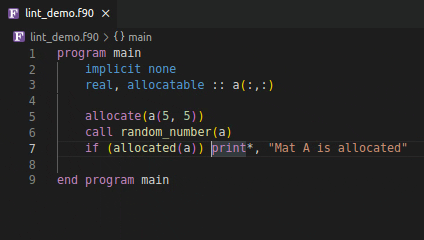
Using incorrect type and rank as function argument
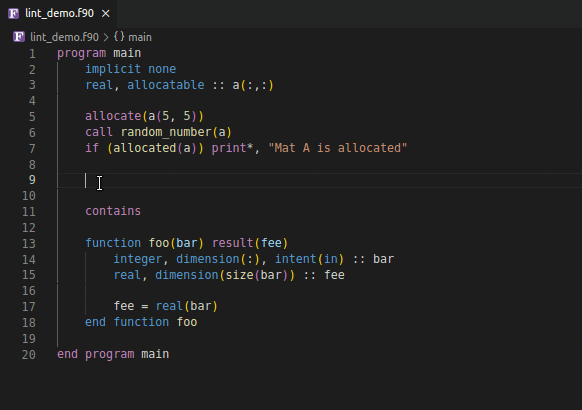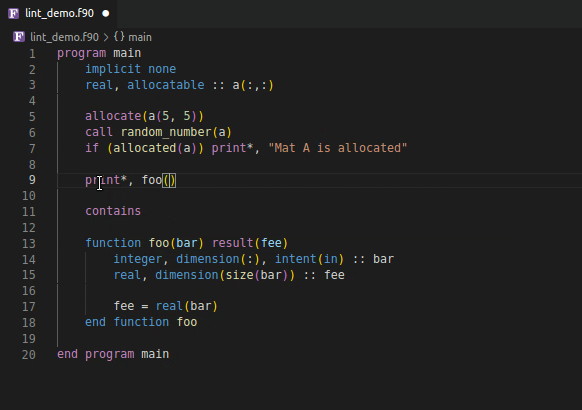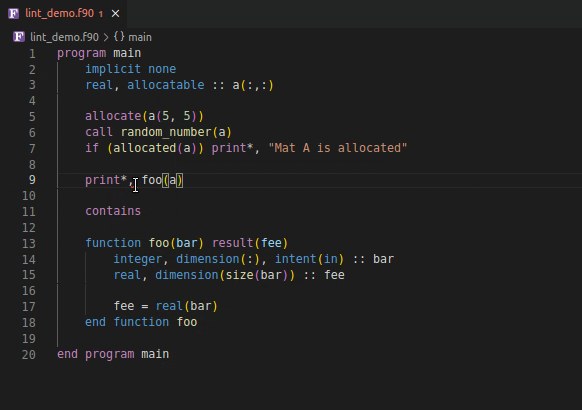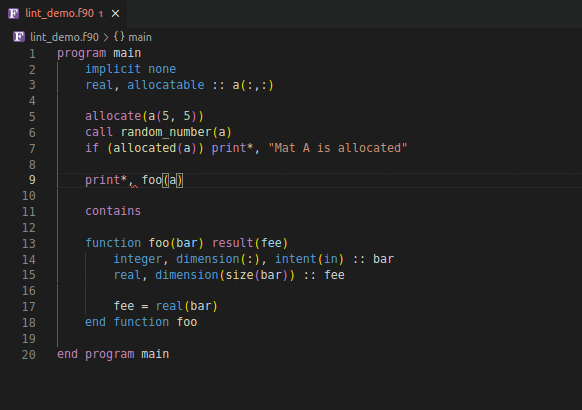
| 📝️ Note | Save your file to generate linting results | | ——- | —————————————— |
Linting results can be improved by providing additional options to the compiler.
Including directories
You can control the include paths to be used by the linter with the fortran.linter.includePaths option.
| ❗️ Important | For the best linting results linter.includePaths should match the included paths for your project’s compilation. |
| ———— | —————————————————————————————————————— |
{
"fortran.linter.includePaths": ["/usr/include/**", "${workspaceFolder}/include/**"]
}
| ❗️ Important | If a glob pattern is used only directories matching the pattern will be included | | ———— | ——————————————————————————– |
Additional linting options
More options can be passed to the linter via
{
"fortran.linter.extraArgs": [
"-fdefault-real-8",
"-fdefault-double-8",
"-Wunused-variable",
"-Wunused-dummy-argument"
]
}
Default value is -Wall (or -warn all for ifort).
Changing linting compiler
By default, the linter used is gfortran, Intel’s ifort and Intel’s LLVM based compiler ifx are also supported.
One can use a different linter compiler via the option
{
"fortran.linter.compiler": "ifort" | "gfortran" | "ifx" | "Disabled"
}
The linter executable is assumed to be found in the PATH.
In order to use a different executable or if the executable can’t be found in the PATH
you can point the extension to another linter with the fortran.linter.compilerPath option.
{
"fortran.linter.compilerPath": "/opt/oneapi/compiler/2022.0.2/linux/bin/intel64/ifort"
}
Debugging
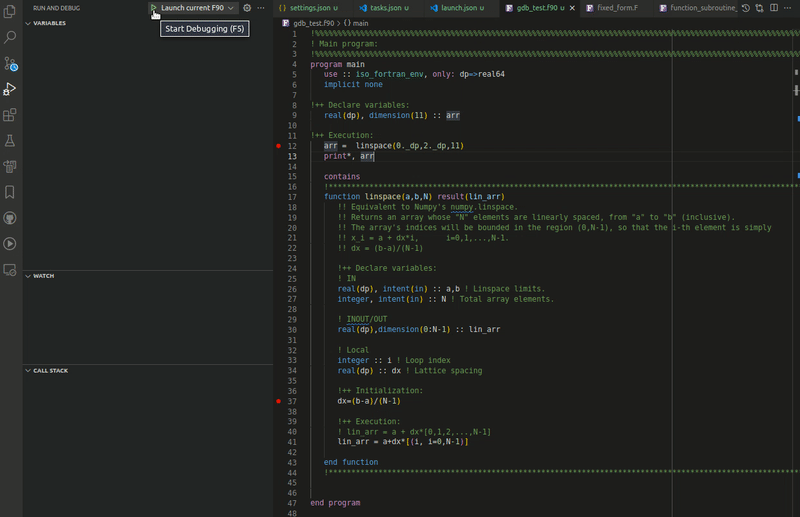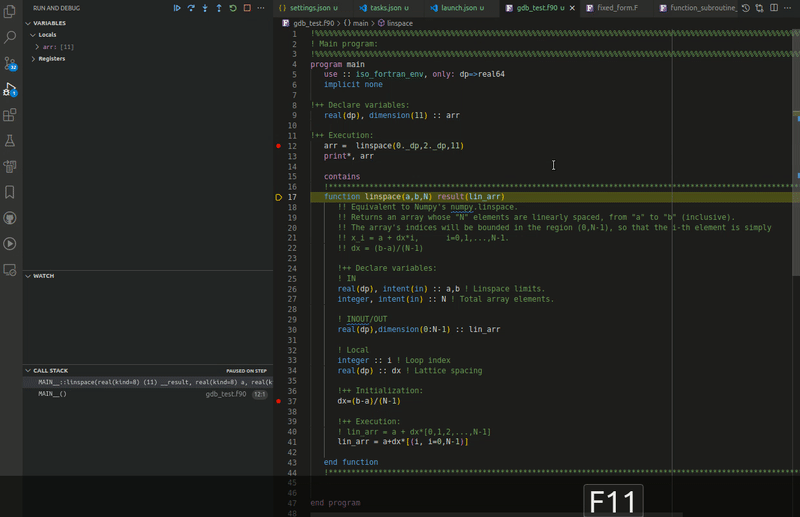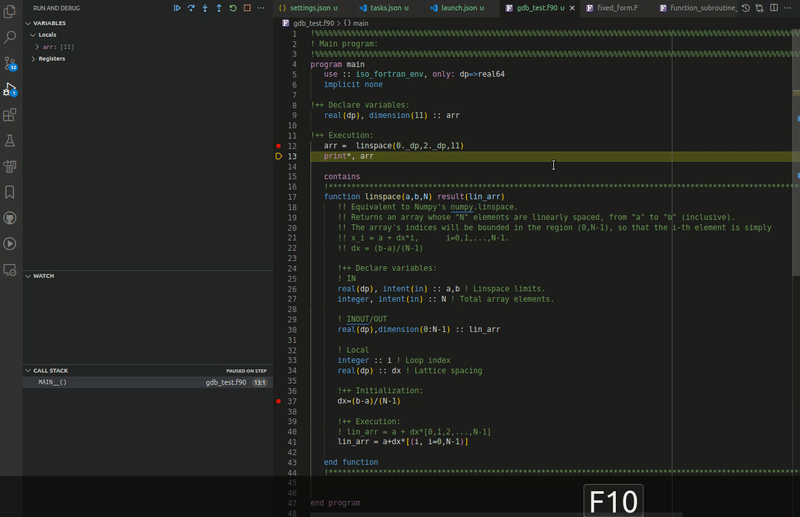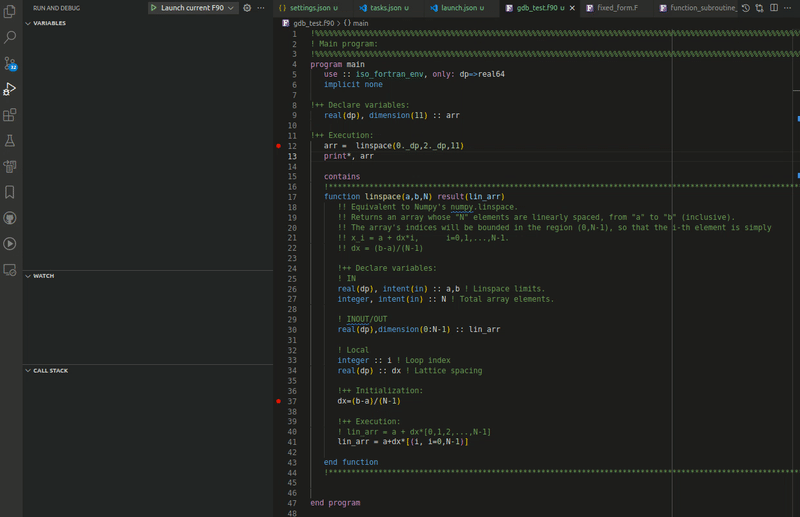
Modern Fortran works with multiple VS Code debuggers and supports the usual debugging tools: conditional and regular breakpoints, expression evaluation, multithreaded debugging, call stack view, step controls, and a watch window.
Supported debugger extensions:
- Microsoft’s C/C++ extension (ms-vscode.cpptools)
- Eclipse’s CDT GDB extension (eclipse-cdt.cdt-gdb-vscode)
- CodeLLDB LLDB extension (vadimcn.vscode-lldb)
| 📝️ Note | For Single file Run/Debug, we pick the first available extension from the list above (top to bottom). | | ——- | ——————————————————————————————————— |
To set up debugging, add a launch.json under .vscode in your workspace. In
VS Code, open the Debug view (Ctrl+Shift+D or Cmd+Shift+D), click the gear, and
choose your debugger from the list.
A minimal launch.json using Microsoft’s
C/C++ extension (ms-vscode.cpptools)
is shown below.
More details on debugging are available on VS Code docs and each extension:
- General information about debugging in VS Code: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/debugging
- C/C++ extension debugger information: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/cpp/cpp-debug
- Build tasks for easy compiling: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/tasks
Example: Launch.json
```jsonc { // Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes. // Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes. // For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387 "version": "0.2.0", "configurations": [ { "name": "(gdb) Fortran", "type": "cppdbg", "request": "launch", "program": "${workspaceFolder}/a.out", "args": [], // Possible input args for a.out "stopAtEntry": false, "cwd": "${workspaceFolder}", "environment": [], "externalConsole": false, "MIMode": "gdb", "setupCommands": [ { "description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb", "text": "-enable-pretty-printing", "ignoreFailures": true, }, ], }, ], } ```Formatting
Two formatters are supported findent
and fprettify. Both of them can be
installed with pip automatically through the extension.
Demo: formatters in action
| findent | fprettify | | :-----------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------: | |  |  |The formatter is controlled by the user option
{
"fortran.formatting.formatter": "findent" | "fprettify" | "Disabled"
}
Additional arguments to the formatter can be input using
{
"fortran.formatting.findentArgs": ["-Cn", "-Rr"],
"fortran.formatting.fprettifyArgs": ["--whitespace-comma", "--enable-decl"]
}
To check all available arguments to formatters try findent -h or fprettify -h
in a terminal.
If the formatter is not present in the PATH its location can be input with
{
"fortran.formatting.path": "./custom/path/venv/bin"
}
| 📝️ Note | findent can also be used to generate dependency files for a project. |
| ——- | ———————————————————————- |
Fortran Package Manager
Validation of fpm.toml
Autocompletion and options validation for fpm.toml files are provided by the
installing the Even Better TOML Visual Studio Code extension.

Snippets
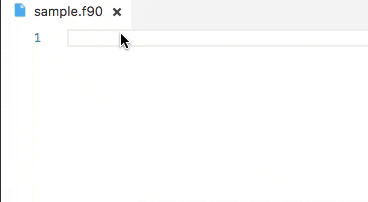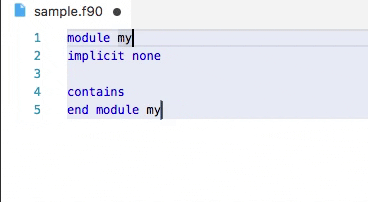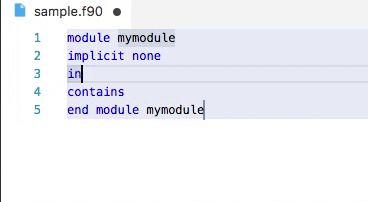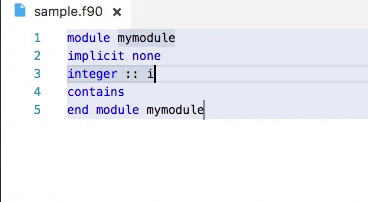
Snippets are included by both fortls Language Server and the Modern Fortran VS Code extension.
Some available snippets can be seen below. Users can define their own snippets
by following these VS Code instructions.
If you think a snippet should be shipped by with the extension feel free to submit a feature request
Demo: snippets in action
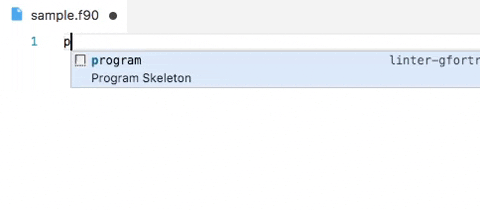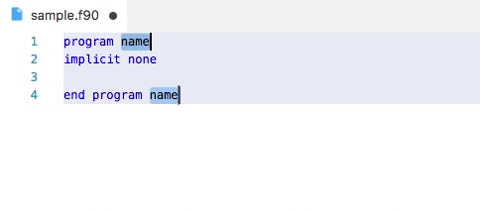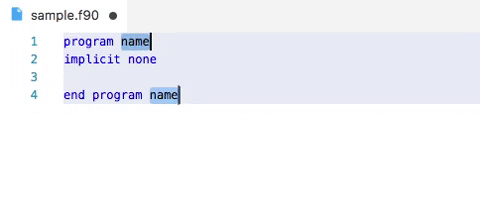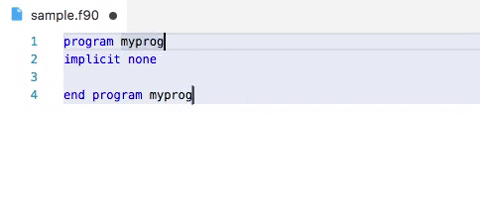
Advanced options
To show the symbols in the file outline enable provide.symbols. Symbols can be
served by the fortls, the built-in, both or none. By default
fortls is used.
{
"fortran.provide.symbols": "fortls" | "Built-in" | "Both" | "Disable"
}
You can also configure the case for fortran intrinsics auto-complete by using
{
"fortran.preferredCase": "lowercase" | "uppercase"
}
Requirements
For debugging you need to have one of the following debuggers installed:
- Linux: GDB
- macOS: GDB or LLDB
- Windows: GDB or Visual Studio Windows Debugger
Contributing
Support Us
You can support further development of the extension by fiscal donations:
 to our LFortan project on NumFOCUS
to our LFortan project on NumFOCUS
Or
 directly sponsoring developers through GitHub Sponsors
directly sponsoring developers through GitHub Sponsors





